Storage
By default, data in Docker containers is only preserved for the duration of the container's lifespan; once the container is removed or destroyed, the data becomes inaccessible. Thus, persistent storage becomes necessary when you need to retain data beyond the lifespan of a container.
Applications that require data persistence, such as databases, file storage systems, or stateful applications, typically rely on persistent storage to store and retrieve data across container restarts or redeployments.
To ensure the persistence of data beyond the container's lifecycle, Docker offers two persistent solutions:
Persistent Storage
Volumes
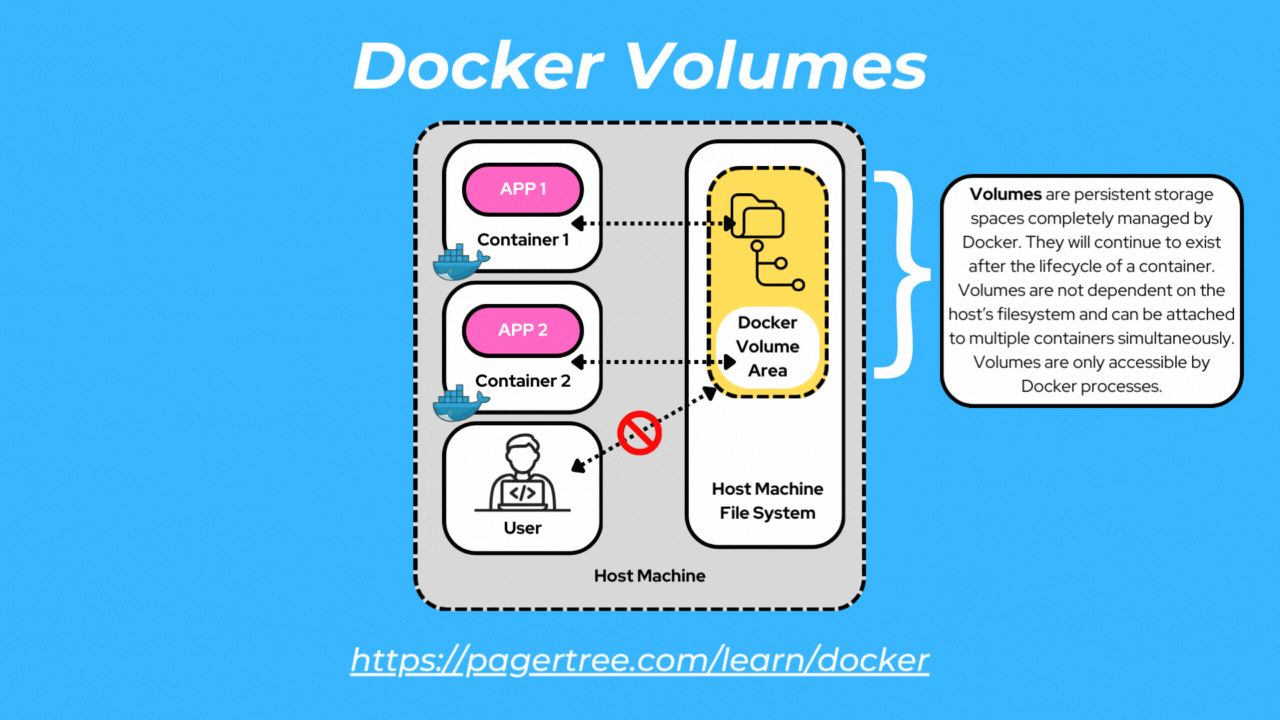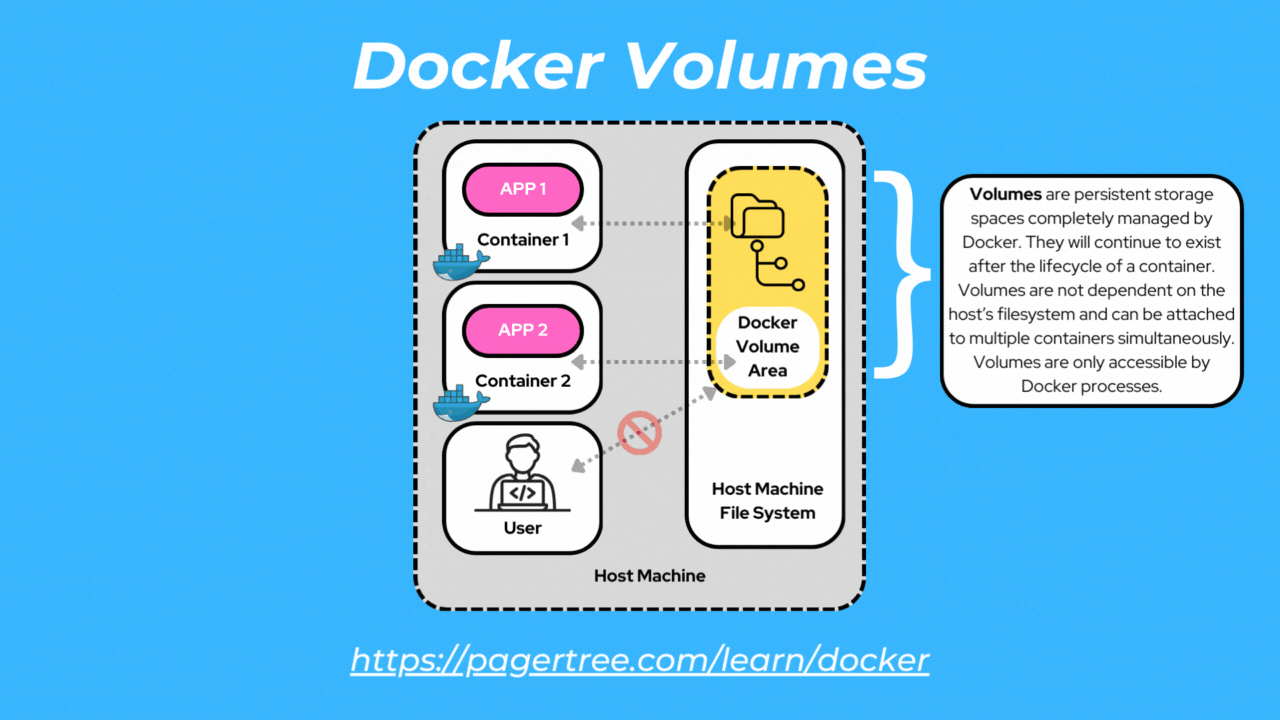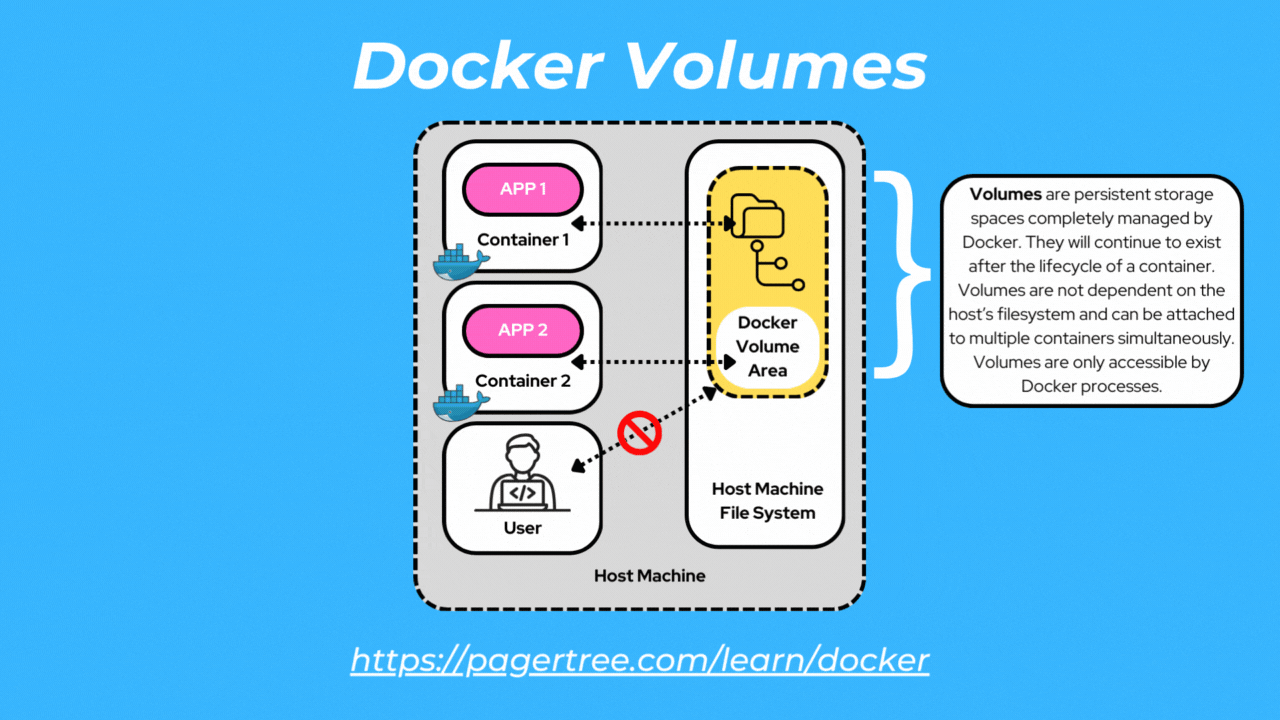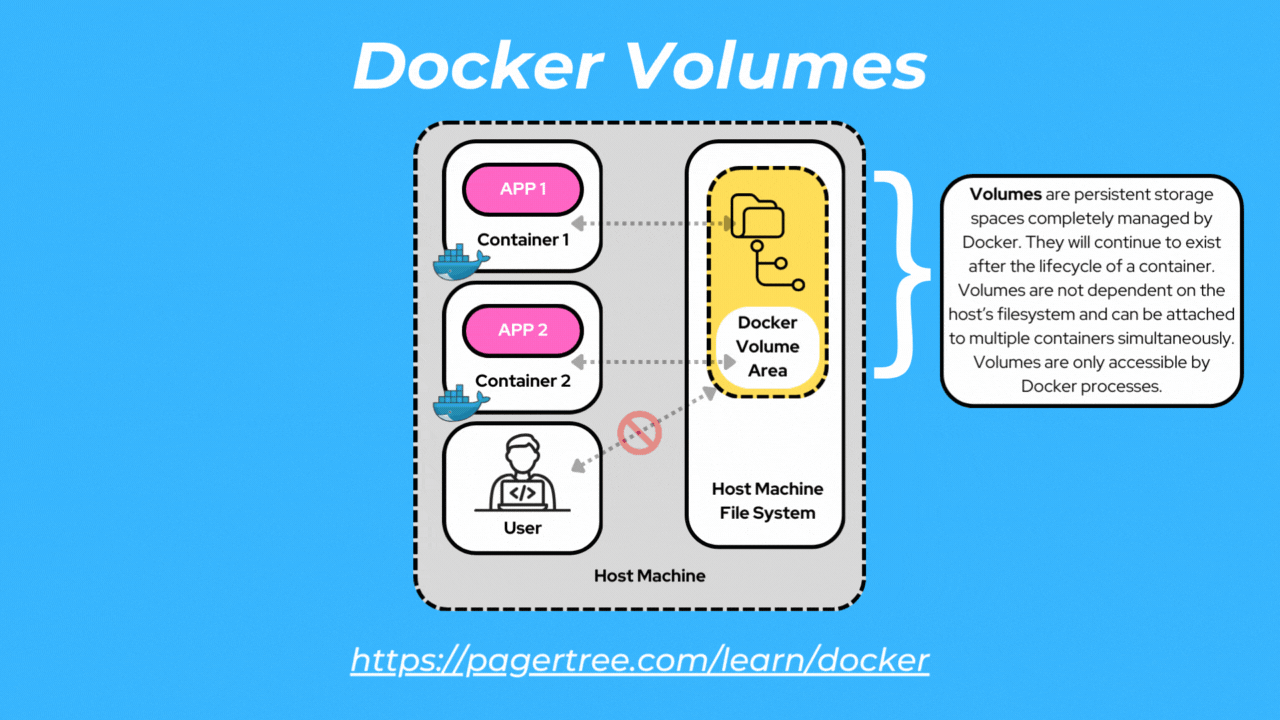
Docker volumes are dedicated storage units managed by Docker. Only Docker containers can access volumes.
Volumes are the preferred way to store container data since they provide efficient performance and are de-coupled from the Docker host.
Volumes are independent of the container's lifecycle and can be easily managed, backed up, and replicated. Additionally, volumes can be attached to multiple containers simultaneously to enable sharing of data and files.
Docker Volumes
Bind Mounts
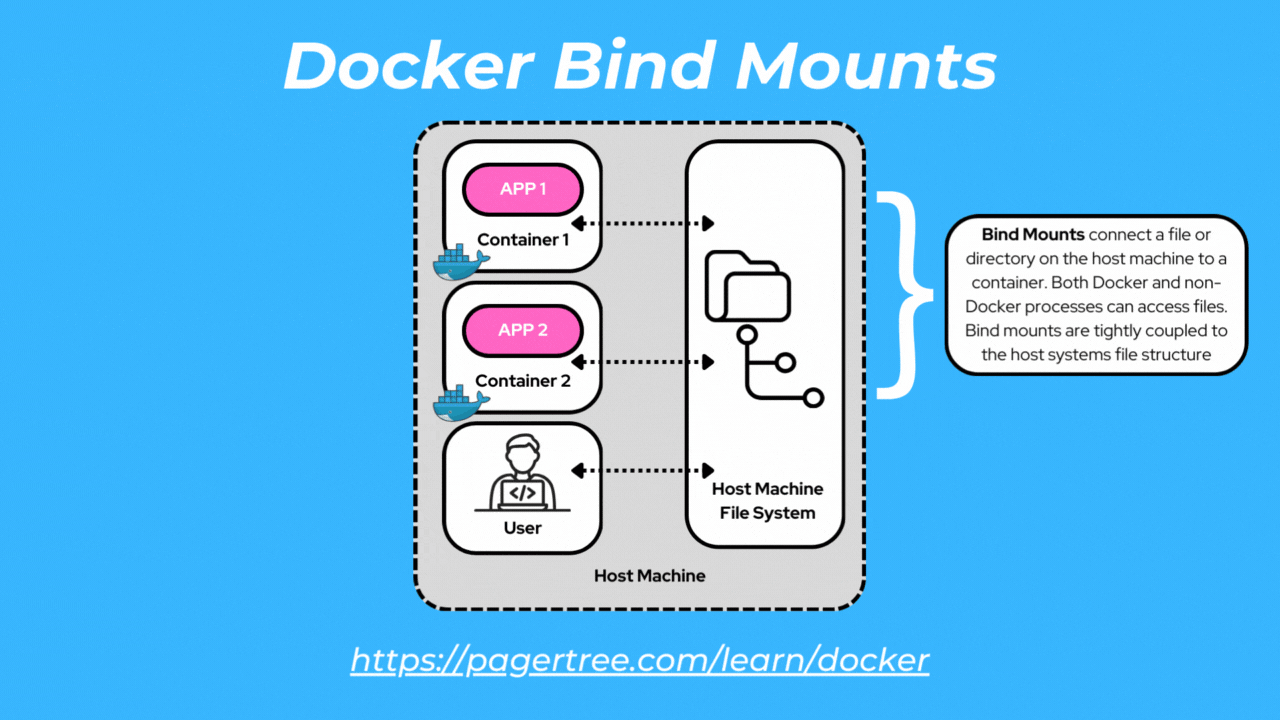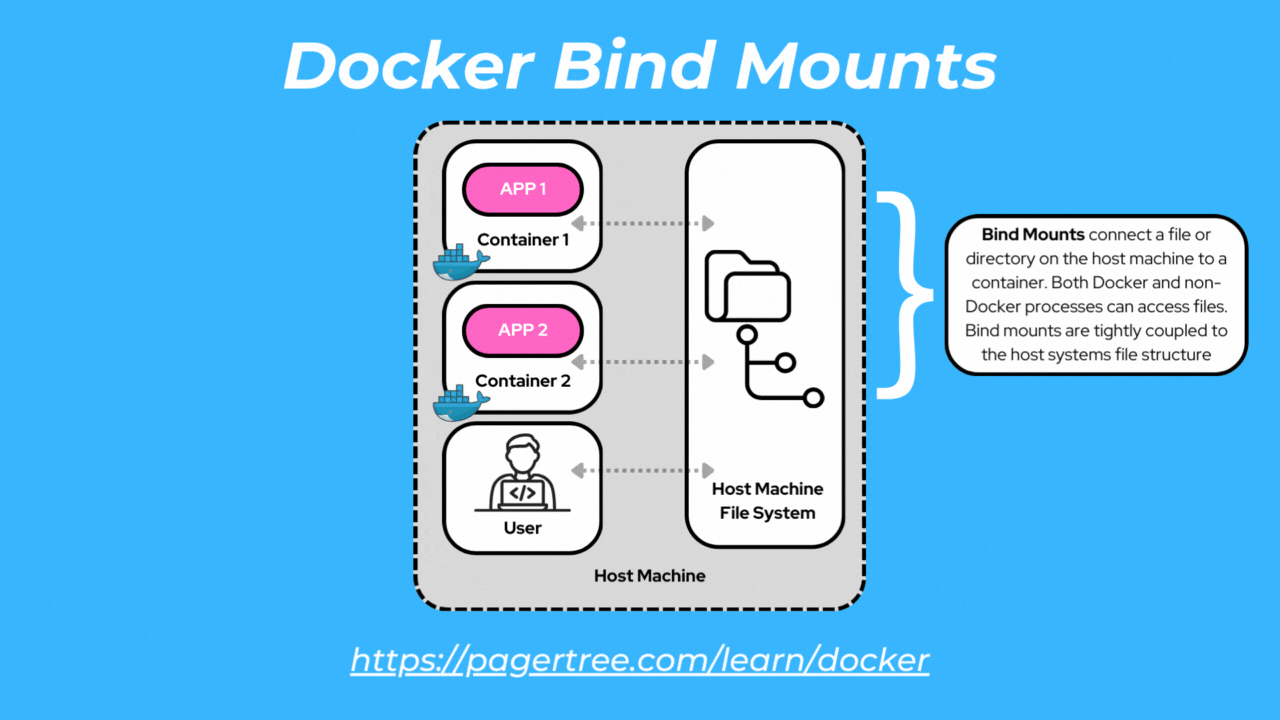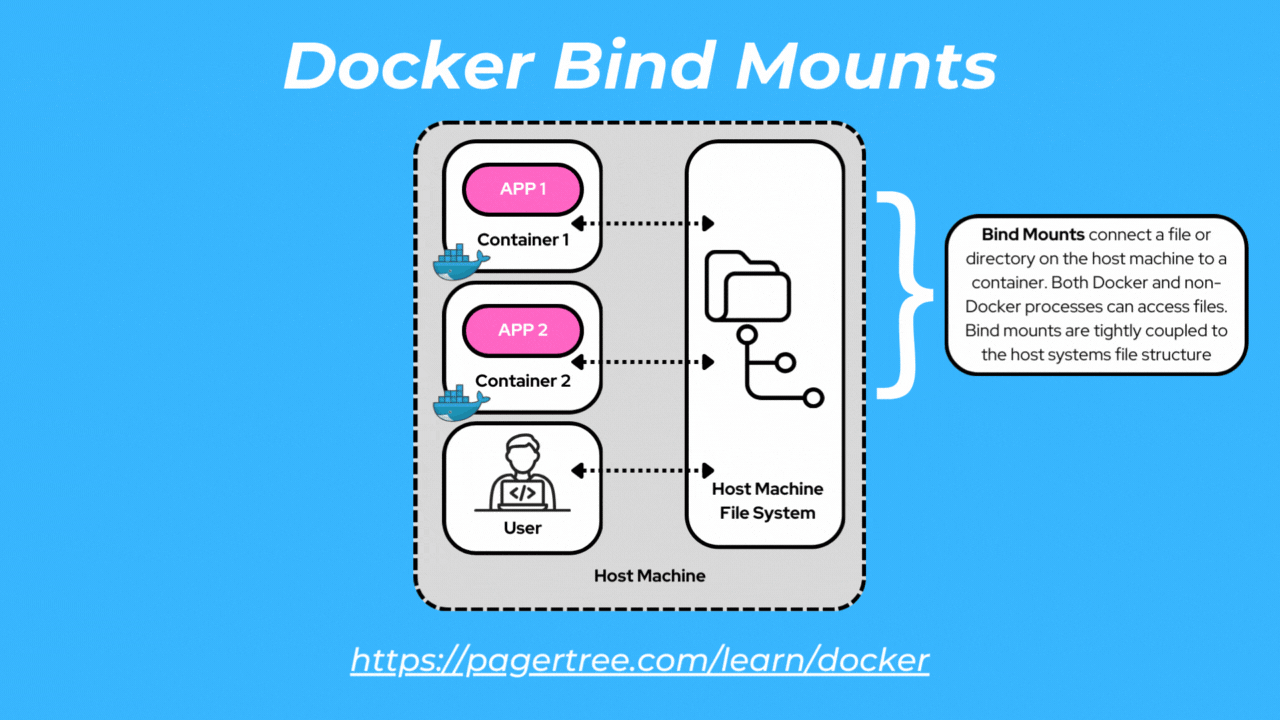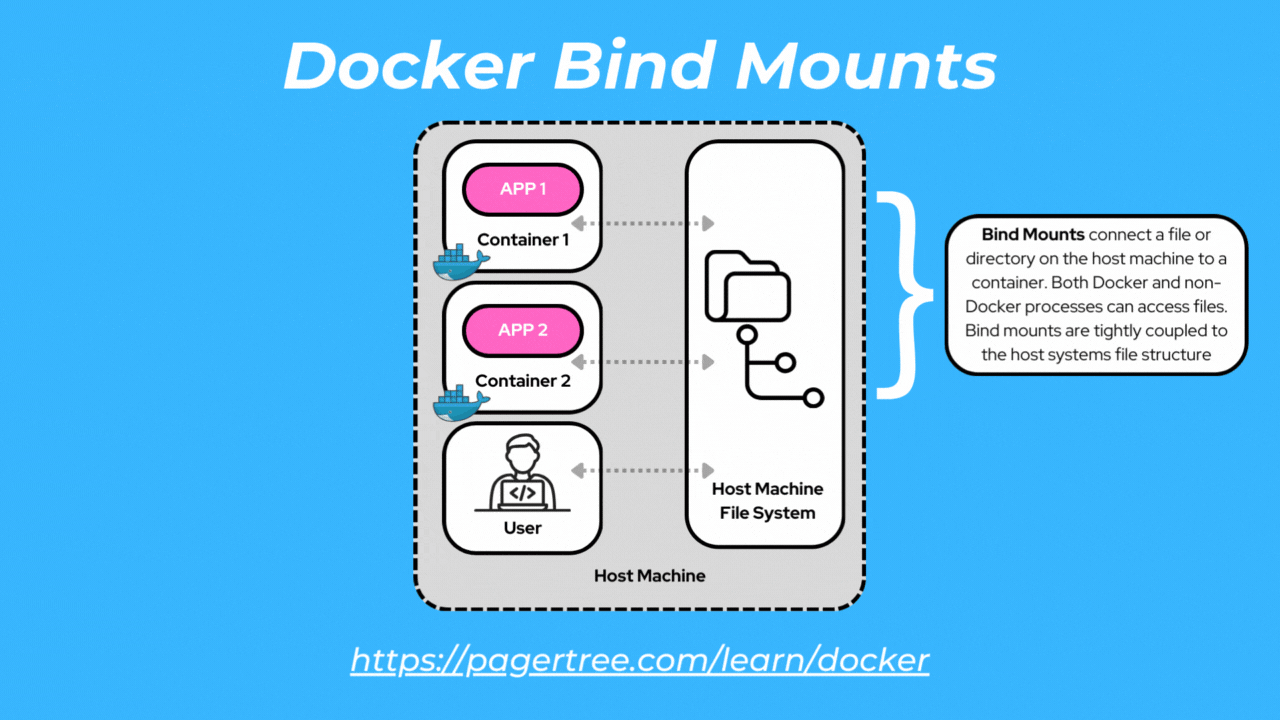
Bind mounts allow you to mount a directory or file from the host machine into a container. Bind mounts can be accessed by both Docker processes and non-Docker processes.
With bind mounts, changes made to files or directories within the container are reflected on the host and vice versa. Bind mounts provide flexibility but are tightly coupled to the host filesystem.
One common scenario where you would use a bind mount is when you are developing a Dockerized application and want to make code changes on your host machine that are immediately reflected within the container without rebuilding the image.
Docker Bind Mounts
Temporary Storage
tmpfs Mounts
tmpfs mounts, or temporary filesystems, are temporary storage areas created in a container's memory space. They are helpful for storing transient data or temporary files within a container (think log files or caching). tmpfs is ephemeral and does not persist data across container restarts. Additionally, you can't share tmpfs mounts between containers.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I Create a Docker Volume?
docker volume create pg-vol
How to Mount a Docker Volume?
To mount a Docker volume, you can use the -v or --volume flag with the docker run command, specifying the volume name and mount path within the container.
docker run -d \
--name pg-server \
--mount source=pg-vol,target=/var/lib/postgresql/data \
postgres:latest
Alternatively, you can define volume mounts in a Docker Compose file using the volumes section (see Docker Volumes with Compose section below).
Where Are Docker Volumes Stored?
Docker volumes are stored in a location managed by Docker, typically within the Docker data directory (default: /var/lib/docker) on the host machine. The specific location depends on the Docker storage driver and configuration settings.
Can Multiple Containers Mount to the Same Volume?
Yes, multiple containers can mount to the same Docker volume simultaneously. This allows multiple containers to share data and collaborate on a common dataset stored in the volume.
What Are Storage Drivers?
Storage drivers extend Docker's native volume functionality by enabling integration with external storage systems or cloud providers. Storage drivers allow you to use specialized storage solutions, such as network-attached storage (NAS), block storage, or cloud storage, as Docker volumes.
Are Docker Volumes Persistent?
Yes, Docker volumes are persistent. They exist independently of the container's lifecycle and are preserved even if the associated container is removed. This makes Docker volumes suitable for storing data that needs to persist across container restarts or redeployments.
Docker Volumes with Compose
In Docker Compose, you can define volumes using the volumes section in your docker-compose.yml file. This allows you to manage volumes and volume mounts declaratively, making it easier to define and configure storage requirements for multi-container applications.
services:
pg-server:
image: postgres:latest
volumes:
- pg-vol:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
pg-vol: