Top 25 DevOps Interview Questions
Since its inception in late 2007 by Project Manager Patrick Debois, DevOps has flourished as an essential practice for any organization looking to improve its software development, deployment, and maintenance practices. Essential jobs like DevOps Engineers are in demand, but as the demand grows, so does the field of candidates. Prepping for your next DevOps interview is the best way to stand out against your competition and ace that next interview.
This guide will cover 25 essential DevOps interview questions, offering clear answers and resources for more learning. We cover fundamental DevOps concepts, practices, and ideas like CI/CD, Infrastructure as Code (IAC), and Deployment processes. We offer additional more in-depth questions interviewers may ask to really test your knowledge and experience in the industry at the end.
- 25 Essential DevOps Interview Questions
- 25 Essential DevOps Interview Questions, Answers, and Resources
- Additional DevOps Interview Questions to Consider
25 Essential DevOps Interview Questions
- What is DevOps?
- What is a DevOps Engineer?
- What are the key skills of a DevOps Engineer?
- What is the DevOps Lifecycle?
- What are the benefits of DevOps?
- What roles and responsibilities are there in DevOps teams?
- Name three important DevOps key performance indicators (KPIs)
- What is the difference between DevOps and Agile?
- What is CI/CD?
- What is the difference between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment?
- What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)?
- What are the benefits of Version Control Systems (VCS)?
- What is the difference between a centralized and distributed version control system?
- What is a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)?
- What is observability?
- What's the difference between observability and monitoring?
- What is Docker?
- What is Prometheus?
- What is a Canary Deployment?
- What are the three main types of cloud computing services?
- What is Continuous Testing, and what are the benefits of Continuous Testing?
- What is Automation Testing, and what are the benefits of Automation Testing?
- What is Incident Management?
- What is High Availability (HA)?
- What are common DevOps tools for each part of the DevOps Lifecycle?
25 Essential DevOps Interview Questions, Answers, and Resources
1. What is DevOps?
DevOps is a set of tools, practices, and philosophies that integrate and automate the work of software development and IT operations teams to improve and shorten the software development cycle.
2. What is a DevOps Engineer?
A DevOps Engineer is a professional who bridges the gap between development and IT operations. They work to streamline and automate the software development and deployment processes through collaboration and championing DevOps practices.
3. What are the key skills of a DevOps Engineer?
While every DevOps Engineer position will have different requirements, all DevOps Engineers should, at a minimum, possess the following key skills:
- Proficiency in Scripting and Programming - Programming languages could include Python, Ruby, Bash, Java, and Node.js.
- Experience with Configuration Management Tools - These tools could include Terraform, Ansible and Puppet to automate and manage configurations.
- Understanding of CI/CD Practices and Tools - Familiarity with CI/CD practices and tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI/CID, and Travis CI.
- Proficiency with Version Control Systems (VCS) - Version control platforms include GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket.
- Experience with Containerization and Orchestration - These tools include Docker and Kubernetes.
- Proficiency with Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Tools - IaC tools could include Terraform, CloudFormation, and Pulumi.
- Experience with Cloud Services - Services include cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Understand of Monitoring and Logging Practices and Tools - Monitoring and logging tools could include Datadog, PRTG, and Prometheus.
- Understanding of Networking - Understanding of network concepts, protocols, and technologies (DNS, HTTP, TCP/IP, VPNs). Knowledge of software-defined networking (SDN) and virtual private networks (VPN).
- Awareness of Security Best Practices/DevSecOps - DevSecOps is the practice of integrating security testing into every aspect of the software development process.
- Excellent Collaboration and Communication Skills - DevOps Engineers require excellent interpersonal skills as they work to constantly bring teams together and champion DevOps practices.
- Focus on Automation - Strong focus on automating repetitive tasks to improve efficiency and reduce errors.
DevOps Engineer Responsibilities
4. What is the DevOps Lifecycle?
- Plan - This stage involves defining and planning the project requirements, understanding customer needs, setting goals, and outlining the project scope.
- Code - Developers write code for the application based on the planned requirements, focusing on creating clean, maintainable, and efficient code.
- Build - The code is compiled and built into executable files or packages, including code review and integration.
- Test - Automated and manual tests are conducted to ensure the code functions as expected, helping identify and fix bugs early in the lifecycle.
- Release - The build is marked as "release" and then stored in a central image repository. A central image repository ensures there is always a releasable version. The team schedules the deployment based on the organization's needs.
- Deploy - Code changes are deployed to production or staging environments, with Continuous Deployment (CD) practices ensuring frequent and reliable deployments.
- Operate - The release is now live and in use by customers. Teams may use software like feature flags to slowly release new features to customers.
- Monitor - Monitoring provides insights into application performance and availability, using feedback to improve future releases and detect anomalies early.
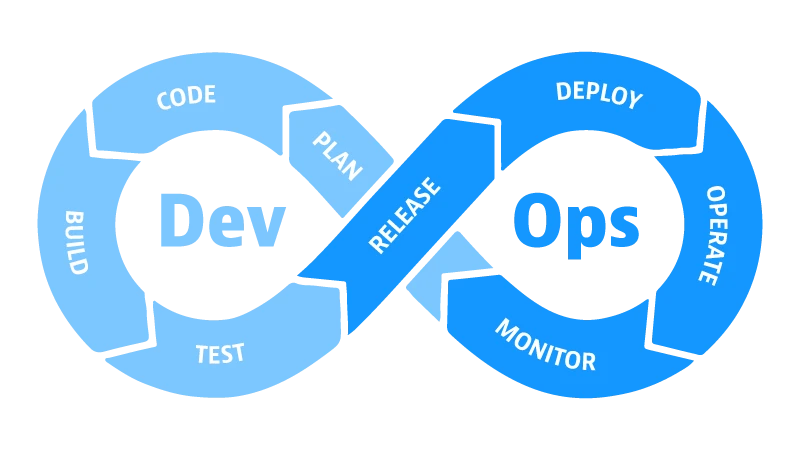
DevOps Lifecycle
5. What are the benefits of DevOps?
- Speed - DevOps practices enable faster software development and delivery by automating processes, reducing manual interventions, and streamlining workflows.
- Scale - DevOps allows organizations to scale their infrastructure and applications efficiently through automation and orchestration tools. This scalability ensures that applications can handle increased loads and growing user demands without compromising performance.
- Improved Collaboration - DevOps fosters a culture of collaboration and communication between development and operations teams. By breaking down silos, it encourages joint problem-solving, shared responsibilities, and better alignment on goals, leading to more cohesive and productive teams.
- Security - DevSecOps integrates security practices into the DevOps pipeline, ensuring that security is a priority throughout the software development lifecycle.
- Reliability - DevOps practices improve application reliability by implementing continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), automated testing, and monitoring. These practices ensure that code changes are thoroughly tested and deployed consistently, reducing the risk of failures and downtime in production environments.
6. What roles and responsibilities are there in DevOps teams?
DevOps Engineer:
- Implements and manages the CI/CD pipeline.
- Automates tasks and processes to improve efficiency.
- Ensures infrastructure is scalable.
- Integrates development and operations efforts.
- Fosters collaboration.
Release Manager:
- Oversees the release process and coordinates releases.
- Plans, schedules, and manages dependencies for releases.
- Ensures smooth and timely delivery of software releases.
Automation Engineer:
- Develops and maintains automation scripts and tools.
- Automates repetitive tasks such as testing, deployment, and infrastructure provisioning.
- Enhances efficiency and reduces manual intervention.
Cloud Engineer:
- Manages and optimizes cloud infrastructure.
- Works with cloud service providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
- Implements cloud-native solutions ensuring scalability, security, and cost-efficiency.
Site Reliability Engineer (SRE):
- Ensures system reliability and performance.
- Focuses on monitoring, incident response, and capacity planning.
- Optimizes system uptime and performance through proactive measures.
Security Engineer:
- Integrates security practices into the DevOps pipeline (DevSecOps).
- Conducts security assessments and implements security tools.
- Ensures compliance with security standards throughout the development lifecycle.
7. Name three important DevOps key performance indicators (KPIs)
-
Deployment Frequency - Measures how often new code is deployed to production. High deployment frequency indicates that the team can deliver new features, improvements, and fixes quickly, reflecting an efficient and effective development process.\
-
Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) - Measures the average time it takes to recover from a failure in production. A lower MTTR indicates that the team can quickly identify, diagnose, and fix issues, maximizing availability and improving system reliability.\
-
Change Failure Rate - Measures the percentage of changes or deployments that result in a failure in production. A lower change failure rate suggests that the team is delivering high-quality code with fewer defects, leading to more stable and reliable releases.
8. What is the difference between DevOps and Agile?
DevOps and Agile are practices aimed at improving the software development process. They differ in focus and scope. Agile primarily centers on the software development phase, emphasizing iterative development, continuous feedback, and collaboration within development teams to deliver small, incremental updates frequently. On the other hand, DevOps goes beyond development to include operations, focusing on the entire software delivery lifecycle from development to deployment and operations. DevOps aims to enhance collaboration between development and operations teams, automate processes, and ensure continuous delivery and integration.
9. What is CI/CD
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (or Continuous Delivery). Continuous Integration involves developers frequently integrating code changes into a shared repository with automated builds and tests to catch issues early, improving software quality and reducing release time.
10. What is the difference between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment?
The difference between Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment lies in the final step of the deployment process. Continuous Delivery ensures the code is always ready for deployment but requires a manual step to release it to production, while Continuous Deployment automates the entire process, deploying changes to production automatically after passing all tests.
11. What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)?
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) is the practice of managing and provisioning computing infrastructure through machine-readable configuration files. This allows for automated and consistent infrastructure deployment.
12. What are the benefits of Version Control Systems (VCS)?
Version Control Systems (VCS) enhance software development by allowing collaboration without overwriting changes and maintaining a history for traceability. They support branching for parallel development, provide backup and recovery, ensure accountability, resolve code conflicts, integrate with CI/CD pipelines, and facilitate code reviews.
13. What is the difference between centralized and distributed version control systems?
A centralized version control system uses a single central repository for all code and version history, making it simple to set up and manage permissions, but it has a single point of failure and potential performance issues. In contrast, a distributed version control system gives every developer a full copy of the repository, allowing for offline work, better performance, and no single point of failure, though it requires more disk space and a more complex setup.
14. What is a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)?
Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) is a specialized discipline under the DevOps umbrella. It blends software engineering principles with infrastructure and operations management. By leveraging automation, deployment strategies, monitoring, observability, and a deep understanding of system architecture, SREs aim to create and maintain scalable, reliable, and efficient software systems.
15. What is observability?
Observability refers to the ability to understand the internal state of a software system based on its external outputs. It involves using data and insights from monitoring to understand the system's health and performance. Observability methods include USE and RED.
-a948e91b9613f8259fcc59eb68b19157.png)
What is Observability?
16. What is the difference between observability and monitoring?
Monitoring is collecting, analyzing, and using data to track the performance, health, and availability of systems and applications, whereas observability is the capability to understand a system’s internal state based on the data it produces, such as logs, metrics, and traces.
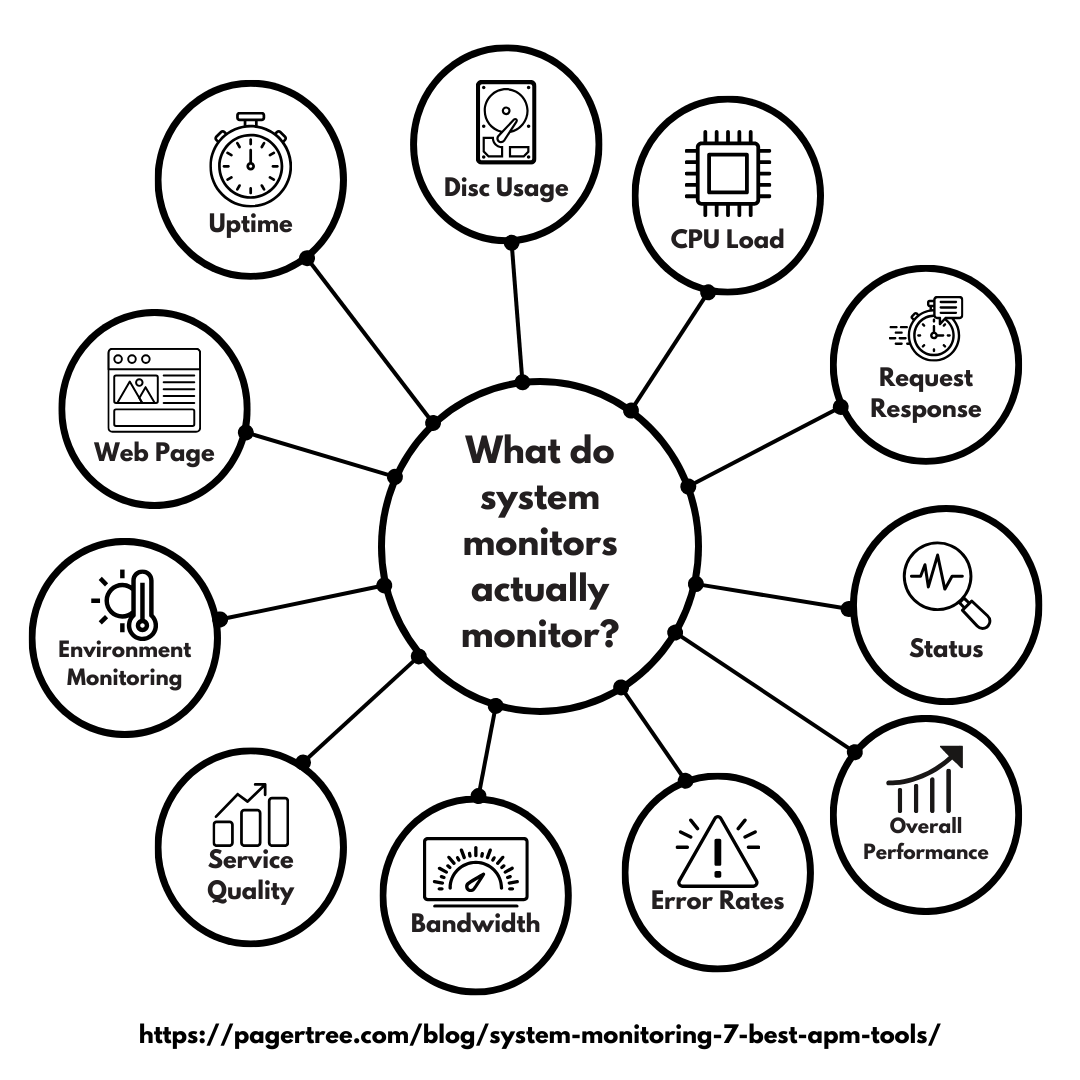
What do system monitors actually do?
17. What is Docker?
Docker is an open-source platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. It allows users to package and run applications in a loosely isolated environment called a container.
18. What is Prometheus?
Prometheus is an open-source systems monitoring and alerting toolkit. It is designed to monitor the health and performance of systems and applications in dynamic cloud-native environments.
19. What is a Canary Deployment?
A Canary Deployment gradually introduces a new software version to a small group of users before a full release, enabling step-by-step validation and reducing the impact of any potential issues.
20. What are the three main types of cloud computing services?
The three main types of cloud computing services are:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - Provides virtualized computing resources like virtual machines and storage (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCE).
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) - Offers a platform for developing, running, and managing applications (e.g., Fly.io, Render, Vercel, and Heroku).
- Software as a Service (SaaS) - Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis (e.g., PagerTree, GitLab, and Salesforce).
21. What is Continuous Testing, and what are the benefits of Continuous Testing?
Continuous Testing is the practice of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release. It involves running tests continuously throughout the development and deployment processes, ensuring that the software is always in a deployable state.
Benefits of Continuous Testing:
- Early Detection of Defects
- Improved Quality
- Faster Time to Market
- Continuous Feedback
- Risk Reduction
- Efficiency and Productivity
22. What is Automation Testing, and what are the benefits of Automation Testing?
Automation Testing is the process of using specialized software tools to execute pre-scripted tests on a software application before it is released into production. The goal is to automate repetitive but necessary tasks in a formalized testing process, replacing manual human intervention.
Benefits of Automation Testing:
- Increased Efficiency
- Improved Accuracy
- Cost Savings
- Enhanced Coverage
- Continuous Testing
- Scalability
23. What is Incident Management?
Incident Management is the process used by DevOps and IT Operations teams to respond to unplanned events or service interruptions (incidents) and restore service to normal as quickly as possible while minimizing business impact.
Incident Management steps include:
24. What is High Availability (HA)?
High Availability (HA) refers to a system's ability to remain operational and accessible for a high percentage of time, often measured in terms of uptime percentage (e.g., 99.99% uptime). It ensures that services remain available and performant even in the event of failures or unexpected disruptions.
25. What are common DevOps tools for each part of the DevOps Lifecycle?
- Planing Tools - JIRA, Trello, Miro
- Coding Tools - Visual Studio Code, GitHub Copilot, GitHub
- Building Tools - Docker, Maven, NPM
- Testing Tools - Selenium, JUnit, TestNG
- Release Tools - Jenkins, Bamboo, GitHub Actions
- Deployment Tools - Terraform, Kubernetes, Ansible
- Operation Tools - Logz.io, Snapshooter, HashiCorp Vault
- Monitoring Tools - Dynatrace, Sumo Logic, Datadog, Prometheus
Additional DevOps Interview Questions to Consider
Interviewers are likely to ask you more in-depth questions that will test your functional knowledge and abilities in the DevOps Engineer role. The following questions will help you consider your previous experience or engage you to think critically about difficult situations.
- Describe a time when you had to use your interpersonal skills to bring a team together or to resolve a conflict.
- Explain the concept of “pair programming” and describe a time you’ve utilized it.
- What challenges are proposed when an organization first starts to implement DevOps practices?
- What is Kubernetes, and what experience do you have with it?
- How do you design a self-healing distributed service?
- What is the difference between a service and a microservice? What is your experience with either?
- How do you measure the success of DevOps implementation?
- What experience do you have with alerting systems like PagerDuty and PagerTree?
Your Next DevOps Role
By familiarizing yourself with these questions and answers, you’ll be well-equipped to demonstrate your knowledge and skills in your next interview. Remember, DevOps is not just about tools and processes; it’s also about fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement. As you advance in your career, continue to explore new technologies, refine your practices, and stay up-to-date with industry trends.
If you're looking at other roles within the DevOps sphere, check out our list of the Top 25 SRE Interview Questions to prepare you for a Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) Role.