Counter Rates & Increases
Counter Resets
Counter metrics can reset to zero when a scraped process restarts (e.g., the server is restarted). Counter functions automatically handle counter resets by assuming that any decrease in a counter value was a reset. Internally, these functions compensate for the reset by adding the last sample value before the reset to all sample values after the reset.
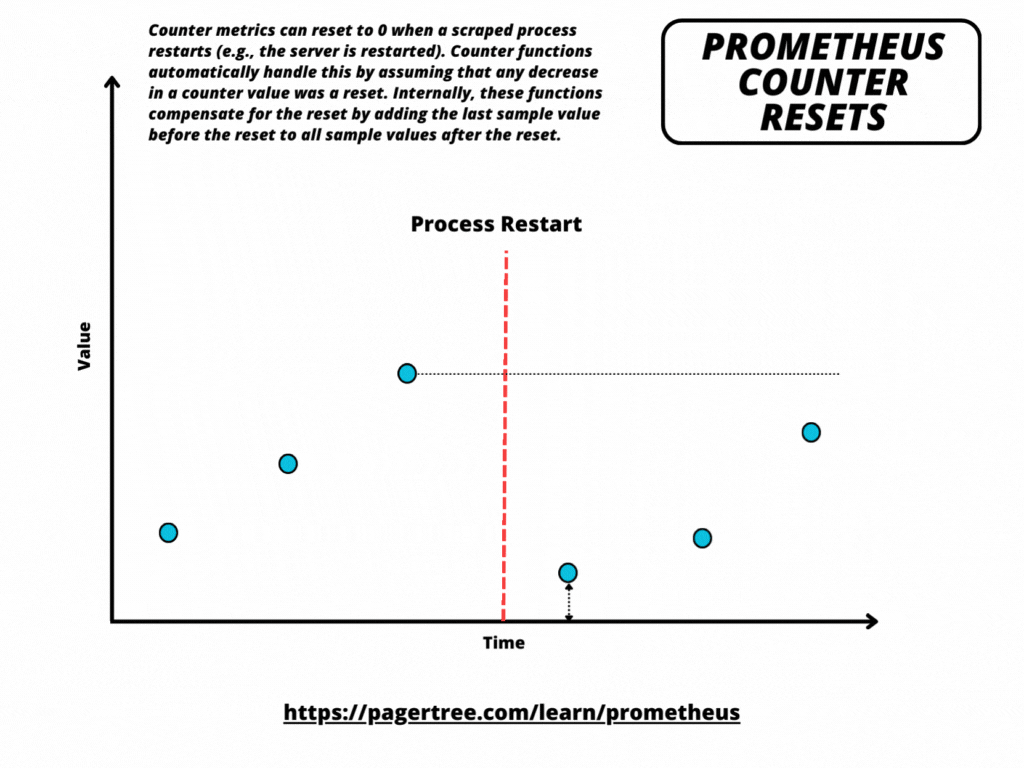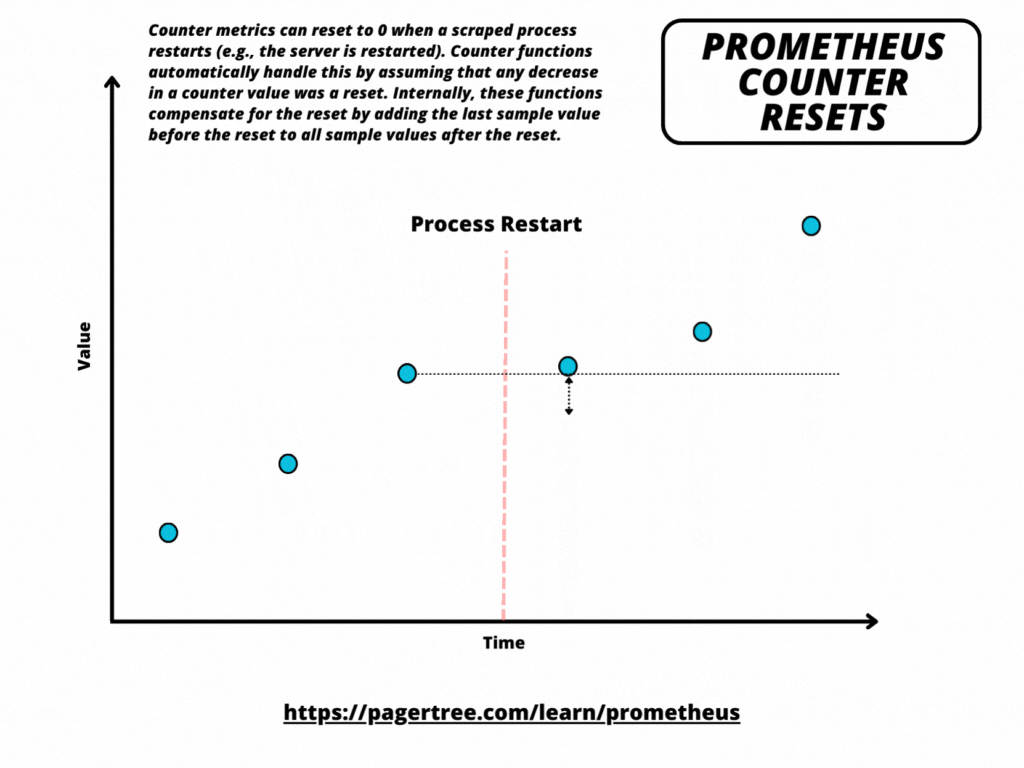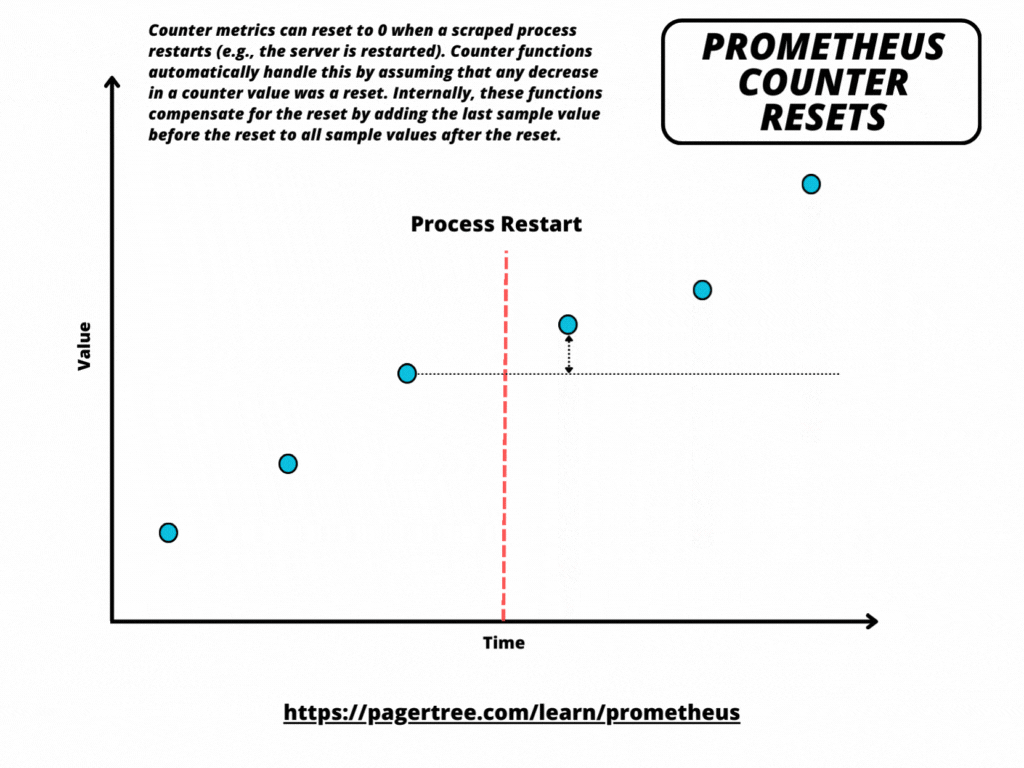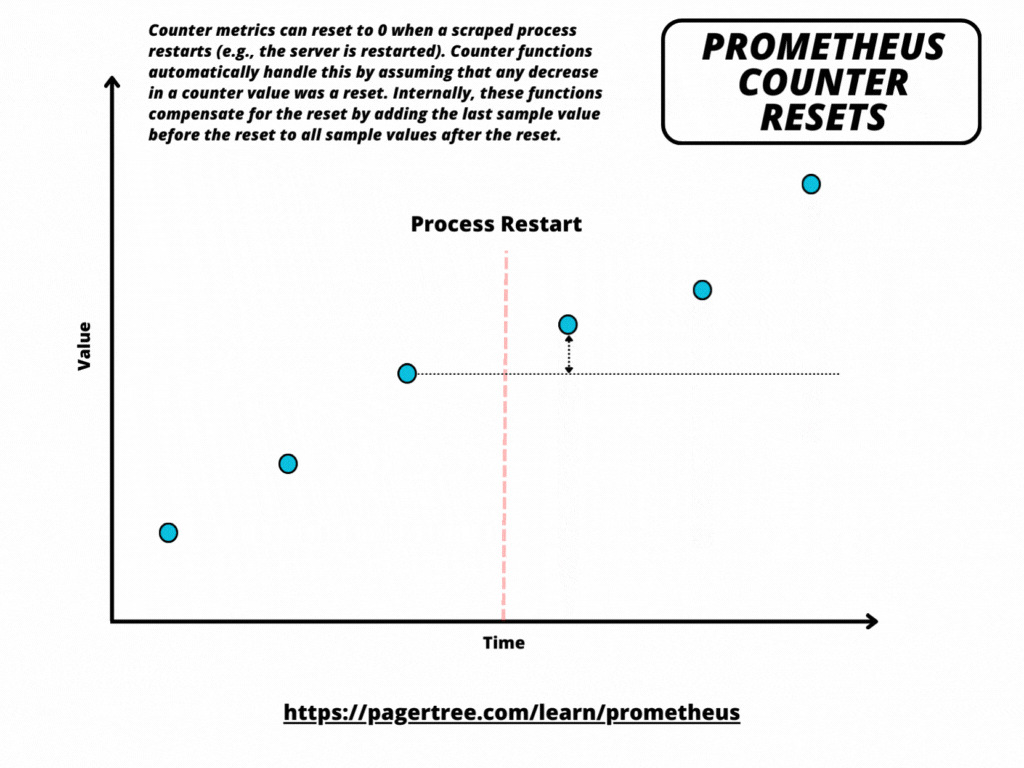
Prometheus Counter Resets Explained Visually
Counter Functions
Rate
rate() - "rate of increase" - calculates a per-second increase of a counter as averaged over a specified window.

PromQL: rate() function
iRate
irate() - "instantaneous rate of increase" - calculates a per-second increase over the time window, only considering the last 2 points.
irate() is much more responsive than rate(). It is good for high-resolution metrics. It should not be used for alerting conditions.

PromQL: irate() function
Increase
increase() - "absolute increase" - calculates the absolute increase over a given time value, including extrapolation.
Logically, only the increase() function includes extrapolation because it measures an absolute increase. rate() and irate() functions calculate a slope (derivative), which will not change even if extrapolation is included.

PromQL: increase() function